SESC源码阅读——Interconnection network
5.Interconnection network
在多处理器系统中,在最低层,每个处理器的caches和贮存都是连接起来的。这些互连行为即是本文的叙述重点。
互连网络涉及到大型多处理器系统中处理器间的交流通道。例子是总线或超立方。
在一个并行机器中,互连网络的工作是将数据从源节点传送到任一期望的目的节点。网络由路由源到目的数据包的开关组成。每一个网络节点包含一个路由表,路由表中存储着网络路径和状态信息,且被用作选择最合适路由向前传递数据包。
5.1 互连网络类
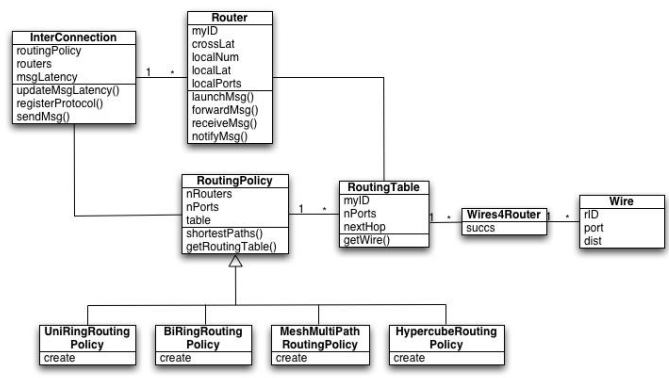
组成SESC网络模型的类的UML表示如下:
//src/libnet/InterConn.h
class InterConnection {
private:
const char *descrSection;
GStatsAvg msgLatency;
ushort linkBits; // link width in bits [1..32700)
float linkBytes; // linkBits / 8
// stores how many routers were already attached to by type of
// object in the network
typedef HASH_MAP<const char *, uint32_t,
HASH<const char*>, SectionComp> ValHash;
ValHash routersCtr;
// stores which port to use based on the object that is attached to
// the network
typedef HASH_MAP<const char *, PortID_t,
HASH<const char*>, SectionComp> PortHash;
PortHash portsCtr;
PortID_t portCtr;
protected:
const char *netType;
RoutingPolicy *rPolicy;//组件1:路由策略
std::vector<Router *> routers;//组件2:路由器
void createRouters();
void destroyRouters();
public:
InterConnection(const char *section);
~InterConnection();
const char *getDescrSection() {
return descrSection;
}
uint32_t getMaxRouters() {
return (uint32_t) routers.size();
}
uint32_t getNextFreeRouter(const char *section);
ushort getLinkBits() {
return linkBits;
}
PortID_t getPort(const char *section);
float getLinkBytes() {
return linkBytes;
}
void updateAvgMsgLatency(Time_t launchTime);
Router *getRouter(RouterID_t id) const {
I(id < routers.size());
return routers[id];
}
// To be removed
size_t getnRouters() const {
return routers.size();
}
// To be removed
PortID_t getnRemotePorts() const;
void registerProtocol(ProtocolCBBase *pcb //!< \param protocol callback to be invoqued when a msg
//arrives to the "device" netID
,MessageType msgType//!< \param message type that netID is listening
,RouterID_t rID //!< \param router where netID is mapped
,PortID_t pID //!< \param port where netID is mapped
,NetDevice_t netID //!< \param device (== protocol) identifier netID
);
void sendMsg(Message *msg) {
RouterID_t rID = msg->getSrcRouterID();
msg->launchMsg(routers[rID]);
}
void sendMsg(TimeDelta_t xlat, Message *msg ) {
RouterID_t rID = msg->getSrcRouterID();
msg->launchMsg(xlat,routers[rID]);
}
void sendMsgAbs(Time_t when, Message *msg) {
RouterID_t rID = msg->getSrcRouterID();
msg->launchMsgAbs(when,routers[rID]);
}
void dumpRouters();
void dump();
};
InterConnection类表示整个网络布局。一个InterConnection对象通过两个组件定义:
- 一组Router对象
- 一个RoutingPolicy对象
5.2 Router类
class Router {
private:
const RouterID_t myID;
// Begin Configuration parameters
const TimeDelta_t crossLat; //!< Router crossing latency [0..32700)
const ushort localNum; //!< Number of addressable local ports [1..MAX_PORTS-LOCAL_PORT1)
const TimeDelta_t localLat; //!< Local port latency [0..32700)
const TimeDelta_t localOcc; //!< Local port occupancy [0..32700)
const ushort localPort;//!< Number of ports for each addressable local port [0..32700)
const bool congestionFree; //!< Skip the router modeling (just local ports)
const TimeDelta_t addFixDelay; //!< fix delay to add to the network forwarding
// End Configuration parameters
PortID_t maxLocalPort;
InterConnection *net; //!< The network where the router is mapped
RoutingTable *rTable;
typedef HASH_MAP<int32_t,ProtocolCBBase*> ProtHandlersType;
ProtHandlersType localPortProtocol;
std::vector<PortGeneric *> l2rPort; //!< ports from local device to router
std::vector<PortGeneric *> r2lPort; //!< ports from router to local device
std::vector<PortGeneric *> r2rPort; //!< ports from router to router (output)
protected:
ushort calcNumFlits(Message *msg) const;
public:
Router(const char *section, RouterID_t id, InterConnection *n, RoutingTable *rt);
virtual ~Router();
void launchMsg(Message *msg); //!< Called when a new message is injected in the router.
void forwardMsg(Message *msg); //!< Called to forward a message from router to router
void receiveMsg(Message *msg); //!< Called when the first flit can arrive to the destination
void notifyMsg(Message *msg); //!< Called when the notification flit arrives to the destination
//!< Register a protocol callback with unique id in the portID
void registerProtocol(ProtocolCBBase *pcb, PortID_t pID, int32_t id);
void dump();
RouterID_t getMyID() const {
return myID;
}
};
Router类表示互连网络中的一个路由器。它根据路由表和ports traffic flow决定将它接收到的数据包往哪发送。
- 每一个Router通过一个ID和一组模型化动态开关行为的参数定义。
- crossLat:通过路由器的延迟
- localLat:本地端口延迟
- localNum:可寻址本地端口的数量(number of addressable local ports)
- localPort:每一个可寻址本地端口的端口数(number of ports for each addressable local port)
一条信息通过launchMsg()函数注入到网络中。forwardMsg()函数将消息从一个路由器发送到另外一个路由器。例如:如果一条消息必须经过五个路由器,则forwardMsg()函数会被调用五次。一旦一条消息到达目的节点,receiveMsg()函数会被调用。每一个路由器在网络中都有它自己的路由表,通过RoutingTable类表示。
//src/libnet/RoutingTable.h
class RoutingTable {
public:
class Wire {
public:
Wire(RouterID_t r
,PortID_t p
,TimeDelta_t d
) {
rID = r;
port = p;
dist = d;
}
RouterID_t rID; // Next Router In that wire
PortID_t port; // Local port to reach routerID
TimeDelta_t dist; // distance to reach routerID
bool operator==(const Wire &w2) {
return rID == w2.rID && port == w2.port && dist == w2.dist;
}
void dump(const char *str) const;
};
protected:
const RouterID_t myID;
const bool fixMessagePath;
const PortID_t nPorts;
class Wires4Router {
public:
Wires4Router() {
prevTurn =0;
}
std::vector<Wire> succs;
int32_t prevTurn;
};
std::vector<Wires4Router> nextHop;
Wire* next; /* next in broadcast (see Message::Type or ask Karin) */
const Wire *getPortWire(RouterID_t id, PortID_t port) const;
//......
}
RoutingTable类拥有一个Wire对象,该对象用于将该路由器与其他各个路由器连接起来。Wire类表示两个路由器间的单向连接。
5.3 RoutingPolicy
RoutingPolicy类是一个抽象类,负责根据给定的网络配置来构建路由表。它拥有五个子类:
- FullyConnectedRoutingPolicy:全连接网络
- UniRingRoutingPolicy:单向环
- BiRingRoutingPolicy:双向环
- HypercubeRoutingPolicy:超立方mesh
- MeshMultiPathRoutingPolicy:多路径路由mesh(新增)
class RoutingPolicy {
protected:
const size_t nRouters;
const size_t nPorts;
const TimeDelta_t crossLat;
const TimeDelta_t wireLat;
std::vector<RoutingTable *> table;
class MyWire : public RoutingTable::Wire {
public:
MyWire() : RoutingTable::Wire(0,DISABLED_PORT,0) {
}
};
std::vector< std::vector< std::vector<MyWire> > > adjacent;
std::vector<MyWire*> next;
void shortestPaths(RouterID_t dst);
RoutingPolicy(const char *section, size_t ports);
void make(const char* section);
virtual void create() = 0;
public:
virtual ~RoutingPolicy() {
}
RoutingTable *getRoutingTable(RouterID_t id) {
I(id<table.size());
return table[id];
}
PortID_t getnRemotePorts() const { return (PortID_t)nPorts; }
void dump() const;
size_t getnRouters() const {
return nRouters;
}
};
class FullyConnectedRoutingPolicy : public RoutingPolicy {
protected:
void create();
public:
FullyConnectedRoutingPolicy(const char *section)
: RoutingPolicy(section,SescConf->getRecordSize("","cpucore") - 1)
{ make(section); }
};
//unidirection ring
class UniRingRoutingPolicy : public RoutingPolicy {
protected:
void create();
public:
UniRingRoutingPolicy(const char *section) : RoutingPolicy(section, 1)
{ make(section); }
UniRingRoutingPolicy(const char *section, size_t ports) : RoutingPolicy(section, ports)
{ /* called from bidirectional ring */ }
};
//bidirectional ring
class BiRingRoutingPolicy : public UniRingRoutingPolicy {
protected:
void create();
public:
BiRingRoutingPolicy(const char *section) : UniRingRoutingPolicy(section,2)
{ make(section); }
};
class MeshMultiPathRoutingPolicy : public RoutingPolicy {
private:
const size_t width;
protected:
void create();
public:
MeshMultiPathRoutingPolicy(const char *section)
: RoutingPolicy(section,4)
,width(SescConf->getInt(section, "width")) {
SescConf->isBetween(section, "width",1,128);
make(section);
}
};
class HypercubeRoutingPolicy : public RoutingPolicy {
protected:
void create();
public:
HypercubeRoutingPolicy(const char *section)
: RoutingPolicy(section, log2i((int)SescConf->getRecordSize("","cpucore")))
{
SescConf->isPower2(section,"hyperNumProcs");
make(section);
}
};